中国沙漠 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (1): 61-74.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00068
收稿日期:2023-03-12
修回日期:2023-05-16
出版日期:2024-01-20
发布日期:2023-12-26
通讯作者:
杨保
作者简介:杨保(E-mail: yangbao@lzb.ac.cn)基金资助:Received:2023-03-12
Revised:2023-05-16
Online:2024-01-20
Published:2023-12-26
Contact:
Bao Yang
摘要:
祁连山及其周边地区是季风-西风交互作用的敏感区,气候变化机制复杂。在研究区域进行了为期一年的参数化方案组合敏感性试验,从5组方案组合中选出模拟效果最佳的参数化方案组合,利用偏差校正过的CMIP6数据驱动最佳参数化方案组合设置下的区域气候模式WRF,对祁连山及周边地区开展了2005—2014年间为期10 a的动力降尺度模拟。结果显示:(1)WRF模式对气温的模拟普遍较好,不同的参数化方案组合对气温的模拟影响不大。WRF模式对降水的模拟受参数化方案组合影响较大,模拟精度整体较气温差。参数化方案组合的敏感性试验结果显示:Thompson云微物理方案、Grell-D积云对流方案、RRTM-Dudhia辐射物理方案和 Noah 陆面过程方案的参数化方案组合最适用于祁连山及周边地区。地形资料敏感性试验结果显示高分辨率地形数据集对气温与降水的模拟未见明显改善。(2)模拟气温与降水的空间分布特征基本能够再现真实观测数据的空间分布特征。气温与降水的空间分布受海拔影响很大,在高海拔地区气温比周围低海拔地区偏低,降水量则是偏高,模拟气温与观测气温之间的相关性好于对降水的模拟。模拟偏差主要表现在对气温的模拟普遍存在低估,对降水量的模拟存在高估。在站点尺度上,模拟温度和降水与观测温度和降水都有着几乎一致的正态分布,各站点上的温度模拟偏差主要出现在冬季,降水模拟偏差则出现在夏季。
中图分类号:
李霞, 杨保. 祁连山及周边地区气温与降水的动力降尺度模拟[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(1): 61-74.
Xia Li, Bao Yang. Dynamic downscaling simulation of temperature and precipitation in the Qilian Mountains and its surrounding areas[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(1): 61-74.
| 方案 | 云微物理过程 | 积云对流 | 长波辐射 | 短波辐射 | 边界层 | 近地层 | 陆面过程 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case A | WSM6 | Kain-Fritsch | CAM | CAM | YSU | MM5 | Noah |
| Case B | WSM6 | Kain-Fritsch | RRTM | Dudhia | YSU | MM5 | Noah |
| Case C | WSM6 | Grell-Devenyi | RRTM | Dudhia | YSU | MM5 | Noah |
| Case D | Thompson | Grell-Devenyi | RRTM | Dudhia | YSU | MM5 | Noah |
| Case E | Thompson | Kain-Fritsch | RRTM | Dudhia | YSU | MM5 | Noah |
表1 参数化方案组合
Table 1 Parametric programme combinations
| 方案 | 云微物理过程 | 积云对流 | 长波辐射 | 短波辐射 | 边界层 | 近地层 | 陆面过程 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case A | WSM6 | Kain-Fritsch | CAM | CAM | YSU | MM5 | Noah |
| Case B | WSM6 | Kain-Fritsch | RRTM | Dudhia | YSU | MM5 | Noah |
| Case C | WSM6 | Grell-Devenyi | RRTM | Dudhia | YSU | MM5 | Noah |
| Case D | Thompson | Grell-Devenyi | RRTM | Dudhia | YSU | MM5 | Noah |
| Case E | Thompson | Kain-Fritsch | RRTM | Dudhia | YSU | MM5 | Noah |
| TM | 地形资料 | 冬季 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | 默认 | 0.8514 | 0.9834 | 0.9811 | 0.9694 |
| SRTM3 | 0.8456 | 0.9848 | 0.9800 | 0.9700 | |
| RMSE | 默认 | 2.1529 | 0.9702 | 1.2508 | 1.0850 |
| SRTM3 | 2.1583 | 0.9122 | 1.3001 | 1.0944 | |
| σ | 默认 | 1.4450 | 1.0548 | 1.1808 | 1.0627 |
| SRTM3 | 1.4336 | 1.0444 | 1.1896 | 1.0751 | |
| PB | 默认 | 23.13% | -43.57% | -4.77% | 10.32% |
| SRTM3 | 22.61% | -43.27% | -4.49% | 4.99% |
表2 两套地形资料的模拟温度评估结果
Table 2 Results of simulated temperature assessment for two sets of topographic data
| TM | 地形资料 | 冬季 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | 默认 | 0.8514 | 0.9834 | 0.9811 | 0.9694 |
| SRTM3 | 0.8456 | 0.9848 | 0.9800 | 0.9700 | |
| RMSE | 默认 | 2.1529 | 0.9702 | 1.2508 | 1.0850 |
| SRTM3 | 2.1583 | 0.9122 | 1.3001 | 1.0944 | |
| σ | 默认 | 1.4450 | 1.0548 | 1.1808 | 1.0627 |
| SRTM3 | 1.4336 | 1.0444 | 1.1896 | 1.0751 | |
| PB | 默认 | 23.13% | -43.57% | -4.77% | 10.32% |
| SRTM3 | 22.61% | -43.27% | -4.49% | 4.99% |
| PR | 地形资料 | 冬季 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | 默认 | 0.5600 | 0.7439 | 0.7488 | 0.8537 |
| SRTM3 | 0.5635 | 0.7671 | 0.7610 | 0.8501 | |
| RMSE | 默认 | 0.1220 | 0.5701 | 1.9509 | 0.5111 |
| SRTM3 | 0.1281 | 0.5527 | 2.5444 | 0.5176 | |
| σ | 默认 | 2.6045 | 1.8488 | 2.3639 | 1.9915 |
| SRTM3 | 2.7283 | 1.8421 | 2.9436 | 2.0027 | |
| PB | 默认 | 278.60% | 79.12% | 89.90% | 62.41% |
| SRTM3 | 283.58% | 85.68% | 114.29% | 67.88% |
表3 两套地形资料的模拟降水评估结果
Table 3 Results of simulated precipitation assessment for two sets of topographic data
| PR | 地形资料 | 冬季 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | 默认 | 0.5600 | 0.7439 | 0.7488 | 0.8537 |
| SRTM3 | 0.5635 | 0.7671 | 0.7610 | 0.8501 | |
| RMSE | 默认 | 0.1220 | 0.5701 | 1.9509 | 0.5111 |
| SRTM3 | 0.1281 | 0.5527 | 2.5444 | 0.5176 | |
| σ | 默认 | 2.6045 | 1.8488 | 2.3639 | 1.9915 |
| SRTM3 | 2.7283 | 1.8421 | 2.9436 | 2.0027 | |
| PB | 默认 | 278.60% | 79.12% | 89.90% | 62.41% |
| SRTM3 | 283.58% | 85.68% | 114.29% | 67.88% |
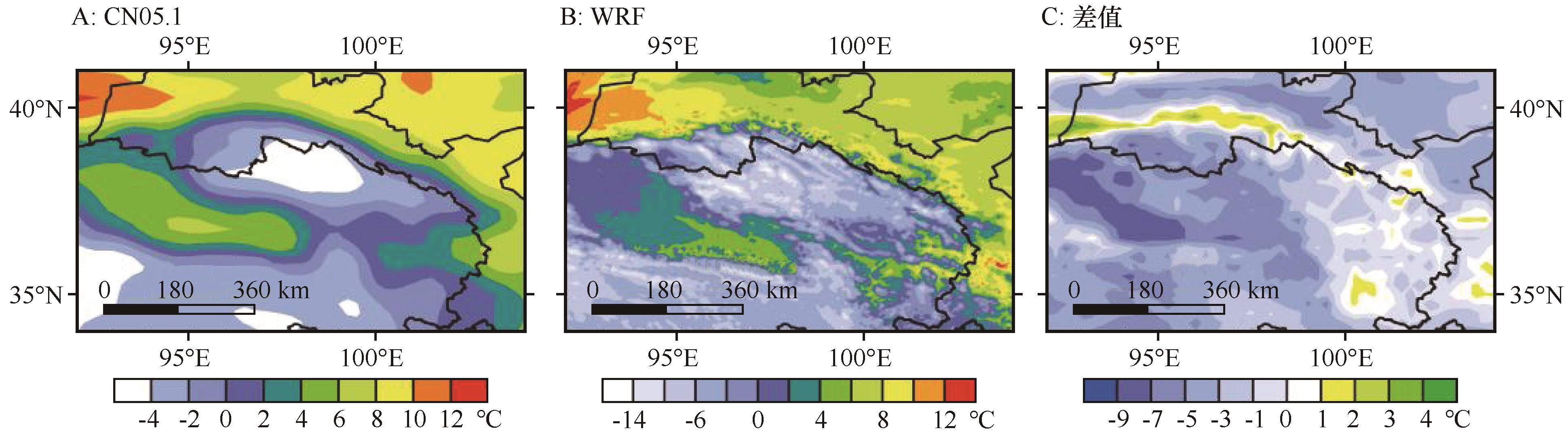
图4 2005—2014年观测(A)和模拟(B)年平均温度及两者之间差值(C)的空间分布
Fig.4 Spatial distribution of observed (A) and modelled (B) annual mean temperatures and spatial distribution of the difference between the two (C) for 2005-2014
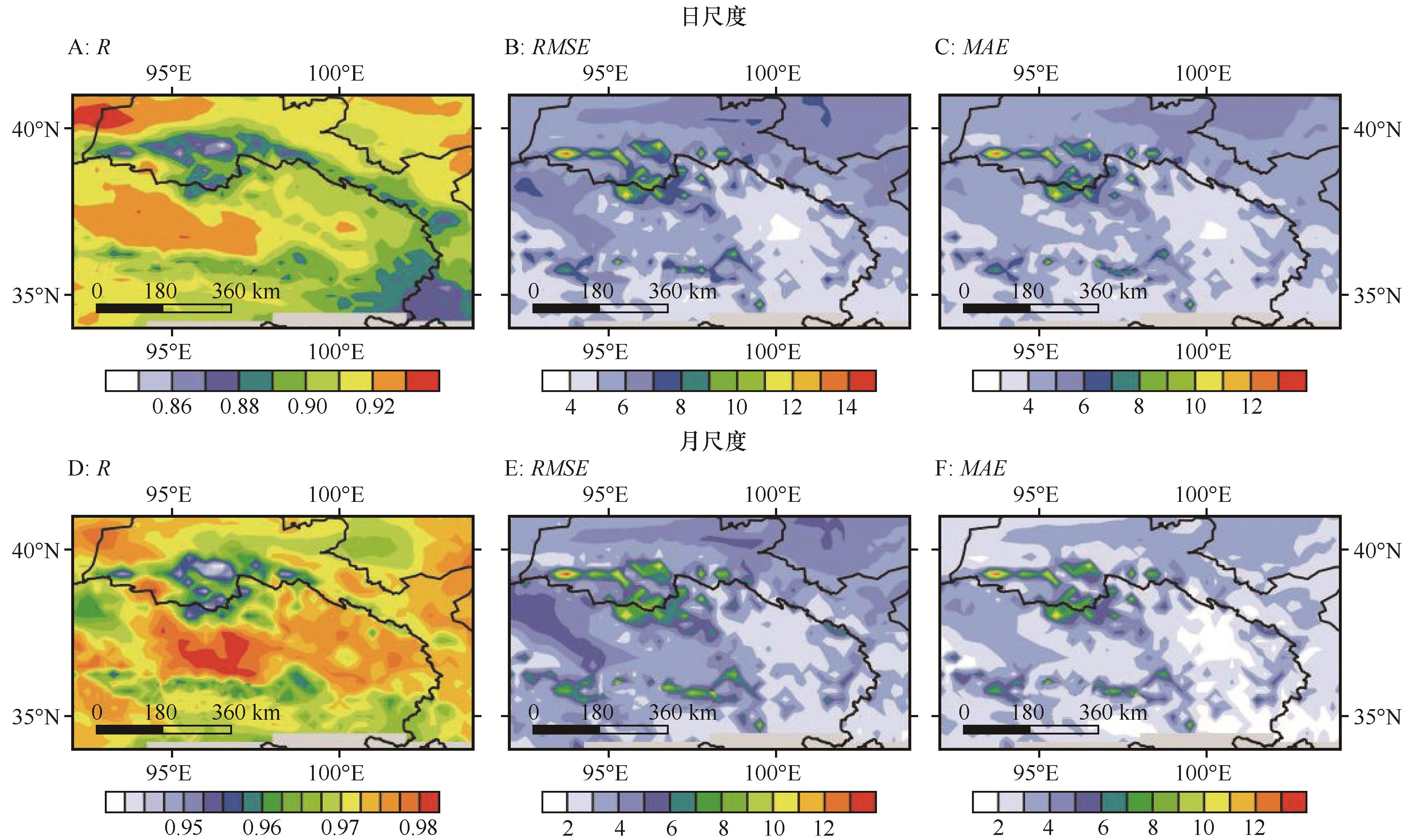
图5 日(A、B、C)、月(D、E、F)尺度温度空间相关系数、均方根误差及绝对偏差空间分布
Fig.5 Spatial distribution of daily(A, B, C) and monthly (D, E, F) scale temperature spatial correlation coefficients, root mean square errors and absolute deviations
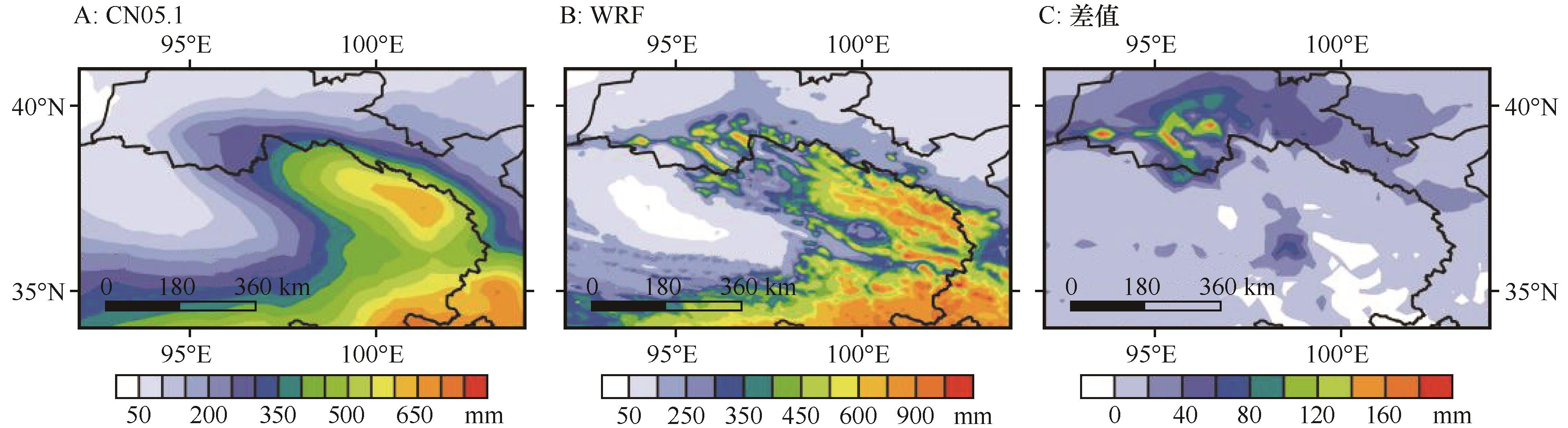
图6 2005—2014年观测(A)和模拟(B)年平均降水量及两者之间差值(C)的空间分布
Fig.6 Spatial distribution of observed (A) and simulated (B) mean annual precipitation and the difference between the two (C) for 2005-2014
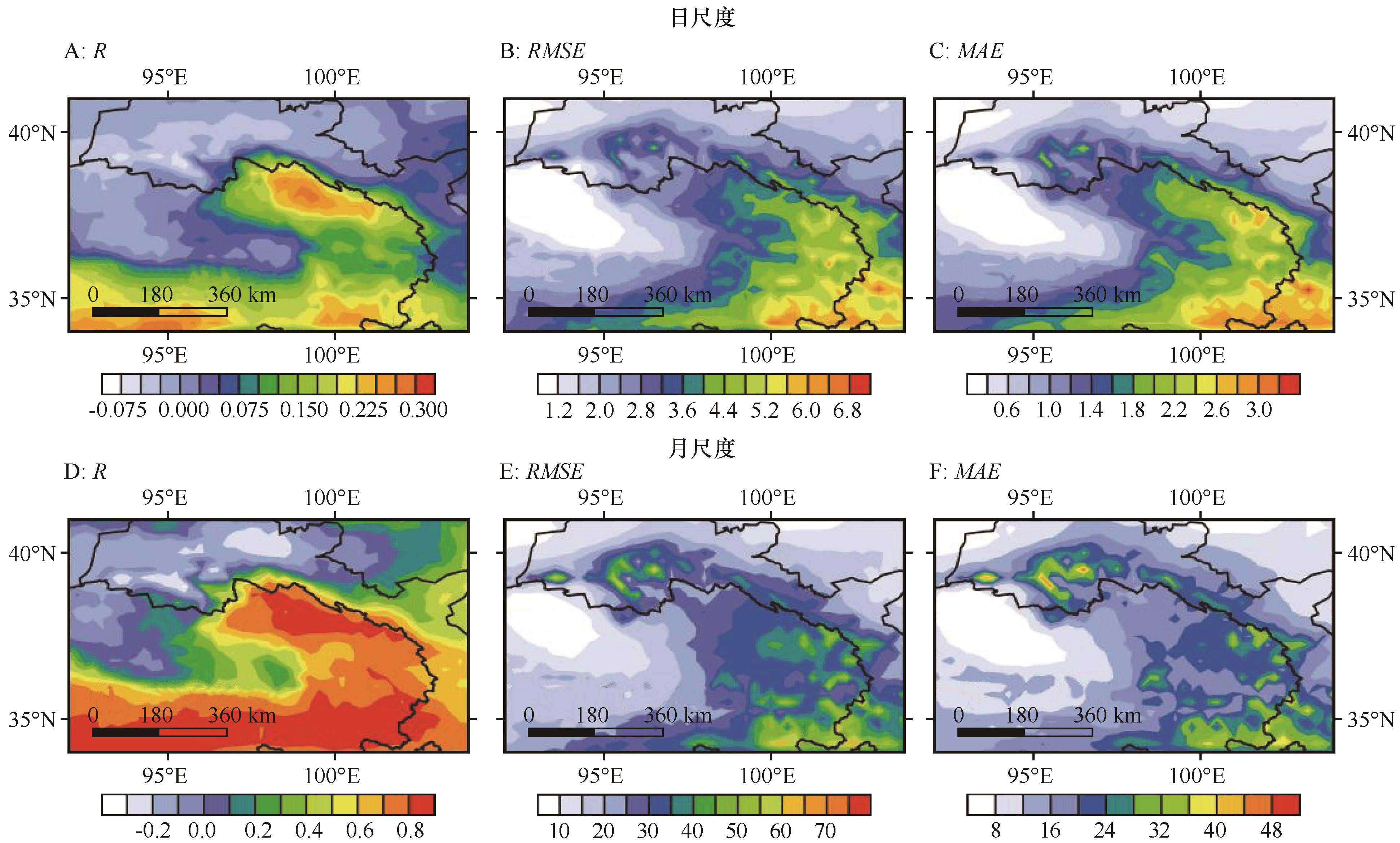
图7 日(A、B、C)、月(D、E、F)尺度降水空间相关系数、均方根误差及绝对偏差空间分布
Fig.7 Spatial distribution of daily (A, B, C) and monthly (D, E, F) scale precipitation spatial correlation coefficients, root mean square errors and absolute deviations
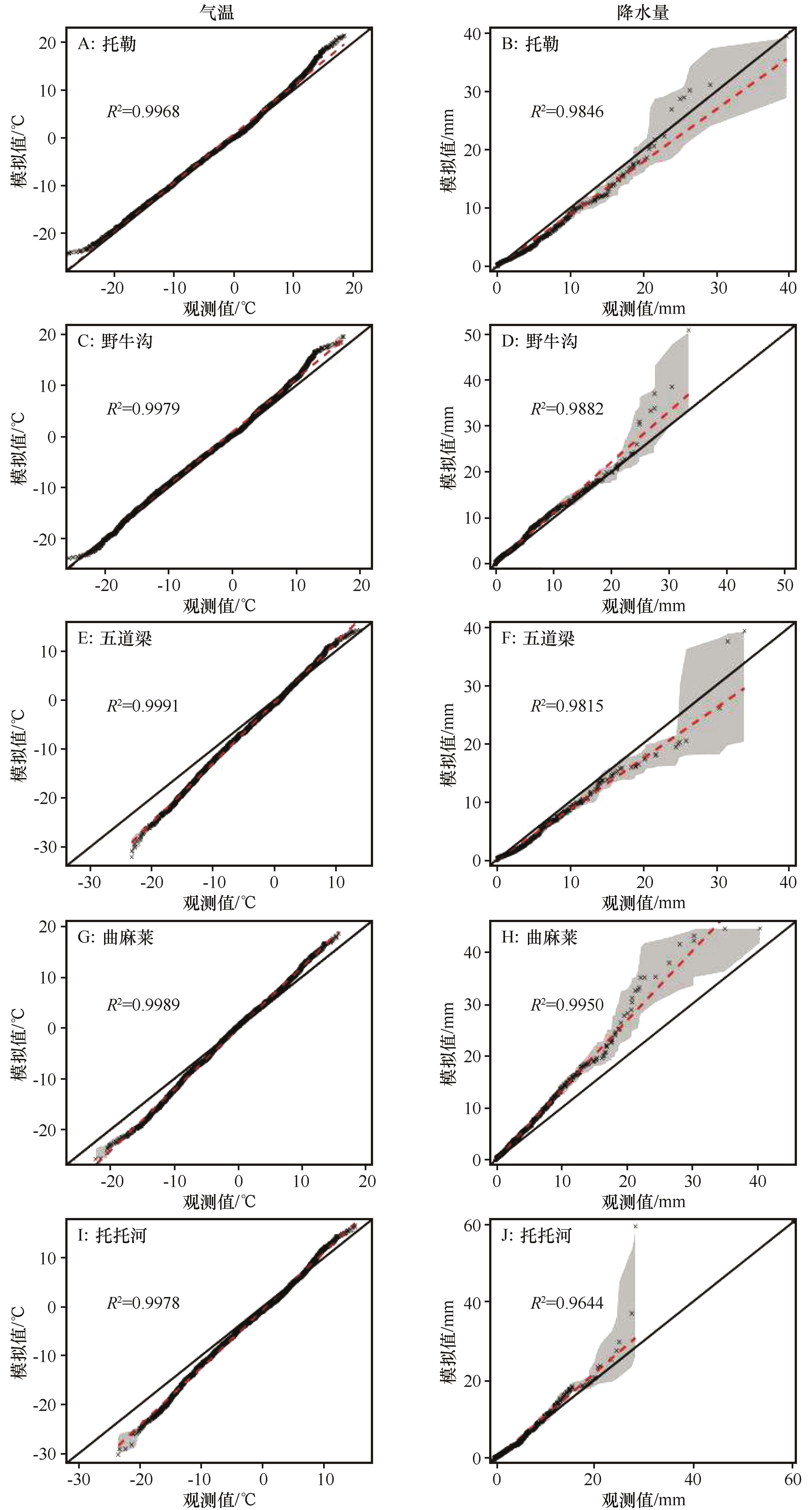
图8 5个站点气温(左)、降水(右)Quantile-Quantile图(灰色阴影范围为90%置信区间)
Fig.8 Quantile-Quantile plots of temperature (left) and precipitation (right) at five sites (Gray shaded region indicates 90% confidence intervals)
| 1 | Xu Z X, Rhoades A M, Johansen H,et al.An intercomparison of GCM and RCM dynamical downscaling for characterizing the hydroclimatology of California and Nevada[J].Journal of Hydrometeorology,2018,19(9):1485-1506. |
| 2 | Corte-Real J, Zhang X B, Wang X L.Downscaling GCM information to regional scales:a non-parametric multivariate regression approach[J].Climate Dynamics,1995,11:413-424. |
| 3 | Lin C G, Chen D L, Yang K,et al.Impact of model resolution on simulating the water vapor transport through the central Himalayas:implication for models' wet bias over the Tibetan Plateau[J].Climate Dynamics,2018,51:3195-3207. |
| 4 | 许建伟,高艳红.WRF模式对夏季黑河流域气温和降水的模拟及检验[J].高原气象,2014,33(4):937-946. |
| 5 | Srinivas C V, Hariprasad D, Rao D V B,et al.Simulation of the Indian summer monsoon regional climate using advanced research WRF model[J].International Journal of Climatology,2013,33(5):1195-1210. |
| 6 | Gao Z B, Yan X D, Dong S Y,et al.Object-based evaluation of rainfall forecasts over eastern China by eight cumulus parameterization schemes in the WRF Model[J].Atmospheric Research,2023:106618. |
| 7 | Wang Y L, Feng J M, Luo M,et al.Uncertainties in simulating central Asia:sensitivity to physical parameterizations using Weather Research and Forecasting model[J].International Journal of Climatology,2020,40(14):5813-5828. |
| 8 | Pérez J C, Díaz J P, González A,et al.Evaluation of WRF parameterizations for dynamical downscaling in the Canary Islands[J].Journal of Climate,2014,27(14):5611-5631. |
| 9 | Argüeso D, Hidalgo-Muñoz J M, Gámiz-Fortis S R,et al.Evaluation of WRF parameterizations for climate studies over southern Spain using a multistep regionalization[J].Journal of Climate,2011,24(21):5633-5651. |
| 10 | Gou D L, Sun J Q, Yu E T.Evaluation of CORDEX regional climate models in simulating temperature and precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau[J].Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters,2018,11(3):219-227. |
| 11 | Wang X J, Pang G J, Yang M X.Precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades:a review based on observations and simulations[J].International Journal of Climatology,2018,38(3):1116-1131. |
| 12 | 韩林君,白爱娟,蒲学敏.基于CMIP6的祁连山气候变化特征预估[J].高原气象,2022,41(4):864-875. |
| 13 | 任婧,张文煜,黄颖,等.祁连山区再分析降水数据的适用性分析[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2023,59(1):23-28. |
| 14 | Gallus W A, Bresch J F.Comparison of impacts of WRF dynamic core,physics package,and initial conditions on warm season rainfall forecasts[J].Monthly Weather Review,2006,134(9):2632-2641. |
| 15 | Jankov I, Gallus Jr W A, Segal M,et al.Influence of initial conditions on the WRF-ARW model QPF response to physical parameterization changes[J].Weather and Forecasting,2007,22(3):501-519. |
| 16 | Crétat J, Pohl B, Richard Y,et al.Uncertainties in simulating regional climate of Southern Africa:sensitivity to physical parameterizations using WRF[J].Climate Dynamics,2012,38:613-634. |
| 17 | Varga Á J, Breuer H.Sensitivity of simulated temperature,precipitation,and global radiation to different WRF configurations over the Carpathian Basin for regional climate applications[J].Climate Dynamics,2020,55(9/10):2849-2866. |
| 18 | 尹金方,王东海,翟国庆.区域中尺度模式云微物理参数化方案特征及其在中国的适用性[J].地球科学进展,2014,29(2):238-242. |
| 19 | 张文煜,任婧,付丹红,等.祁连山一次降水过程云模式模拟参数的选择及微物理结构特征分析[J].干旱区研究,2022,39(6):1717-1727. |
| 20 | 于伟,彭杨,姚礼双,等.WRF模式不同参数化方案对长江上游降雨模拟的影响[J/OL].中国农村水利水电:1-15[2023-03-12].. |
| 21 | 张宝庆,田磊,赵西宁,等.植被恢复对黄土高原局地降水的反馈效应研究[J].中国科学:地球科学,2021,51(7):1080-1091. |
| 22 | Navale A, Singh C, Budakoti S,et al.Evaluation of season long rainfall simulated by WRF over the NWH region:KF vs.MSKF[J].Atmospheric Research,2020,232:104682. |
| 23 | Liu Y, Chen X, Li Q,et al.Impact of different microphysics and cumulus parameterizations in WRF for heavy rainfall simulations in the central segment of the Tianshan Mountains,China[J].Atmospheric Research,2020,244:105052. |
| 24 | Gao S B, Huang D L, Du N Z,et al.WRF ensemble dynamical downscaling of precipitation over China using different cumulus convective schemes[J].Atmospheric Research,2022,271:106116. |
| 25 | Lv M Z, Xu Z F, Yang Z L.Cloud resolving WRF simulations of precipitation and soil moisture over the central Tibetan Plateau:an assessment of various physics options[J].Earth and Space Science,2020,7(2):e2019EA000865. |
| 26 | 周志敏,崔春光,胡扬,等.一次梅雨锋暴雨过程数值模拟的云微物理参数化敏感性研究[J].大气科学,2021,45(6):1292-1312. |
| 27 | 童颖睿,闵锦忠.云微物理方案参数扰动对华北“7.20”暴雨的集合预报试验[J].气象科学,2022,42(2):213-224. |
| 28 | 刘东海,黄静,刘娟,等.国内外典型中尺度数值预报模式参数化方案的综述与展望[J].地球科学进展,2023,38(4):349-362. |
| 29 | 徐娟娟,王可丽,江灏,等.西风与季风扰动对黑河流域降水影响的数值模拟[J].冰川冻土,2010,32(3):489-496. |
| 30 | 宁贵财,尚可政,王式功,等.贺兰山对银川一次致灾暴雨过程影响的数值模拟[J].中国沙漠,2015,35(2):464-473. |
| 31 | 肖林鸿,高艳红, Chen Fei,等.青藏高原极端气温的动力降尺度模拟[J].高原气象,2016,35(3):574-589. |
| 32 | Yang J H, Duan K Q.Effects of initial drivers and land use on WRF modeling for near-surface fields and atmospheric boundary layer over the northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J].Advances in Meteorology,2016(2016):1-16. |
| 33 | Zhang X Z, Xiong Z, Zheng J Y,et al.High-resolution precipitation data derived from dynamical downscaling using the WRF model for the Heihe River Basin,northwest China[J].Theoretical and Applied Climatology,2018,131:1249-1259. |
| 34 | Iacono M J, Delamere J S, Mlawer E J,et al.Radiative forcing by long‐lived greenhouse gases:calculations with the AER radiative transfer models[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2008,113(D13):D13103. |
| 35 | 徐蓉蓉,梁信忠,段明铿.CWRF对青藏高原气温和降水模拟效果的综合评估[J].大气科学学报,2021,44(1):104-117. |
| 36 | Gao Y H, Chen F, Miguez-Macho G,et al.Understanding precipitation recycling over the Tibetan Plateau using tracer analysis with WRF[J].Climate Dynamics,2020,55:2921-2937. |
| 37 | Qian X, Yao Y Q, Wang H S,et al.Validation of the WRF model for estimating precipitable water vapor at the Ali Observatory on the Tibetan Plateau[J].Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific,2020,132(1018):125003. |
| 38 | Dai Y F, Wang L, Yao T D,et al.Observed and simulated lake effect precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau:an initial study at Nam Co Lake[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2018,123(13):6746-6759. |
| 39 | 智协飞,吴佩,俞剑蔚,等.GFS模式地形高度偏差对地面2 m气温预报的影响[J].大气科学学报,2019,42(5):652-659. |
| 40 | 于晓晶,赵勇.地形对天山夏季降水影响的模拟[J].中国沙漠,2016,36(4):1133-1143. |
| 41 | Castro C L, Pielke Sr R A, Leoncini G.Dynamical downscaling:assessment of value retained and added using the Regional Atmospheric Modeling System (RAMS)[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2005,110(D5). |
| 42 | Lo J C F, Yang Z L, Pielke Sr R A.Assessment of three dynamical climate downscaling methods using the Weather Research and Forecasting(WRF)model[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2008,113(D9):D09112. |
| 43 | García-Díez M, Fernández J, Vautard R.An RCM multi-physics ensemble over Europe:multi-variable evaluation to avoid error compensation[J].Climate Dynamics,2015,45(11/12):3141-3156. |
| 44 | Hahmann A N, Vincent C L, Peña A,et al. Wind climate estimation using WRF model output:method and model sensitivities over the sea[J].International Journal of Climatology, 2015,35(12):3422-3439. |
| 45 | Hong S Y, Lim J O J.The WRF single-moment 6-class microphysics scheme (WSM6)[J].Asia-Pacific Journal of Atmospheric Sciences,2006,42(2):129-151. |
| 46 | Thompson G, Field P R, Rasmussen R M,et al.Explicit forecasts of winter precipitation using an improved bulk microphysics scheme.Part II:implementation of a new snow parameterization[J].Monthly Weather Review,2008,136(12):5095-5115. |
| 47 | Kain J S.The Kain-Fritsch convective parameterization:an update[J].Journal of Applied Meteorology,2004,43(1):170-181. |
| 48 | Grell G A, Dévényi D.A generalized approach to parameterizing convection combining ensemble and data assimilation techniques[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2002,29(14):381-384. |
| 49 | Mlawer E J, Taubman S J, Brown P D,et al.Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres:RRTM,a validated correlated‐k model for the longwave[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,1997,102(D14):16663-16682. |
| 50 | Dudhia J.Numerical study of convection observed during the winter monsoon experiment using a mesoscale two-dimensional model[J].Journal of Atmospheric Sciences,1989,46(20):3077-3107. |
| 51 | Collins W D, Rasch P J, Boville B A,et al.Description of the NCAR community atmosphere model (CAM 3.0)[J].NCAR Technical Note,2004,226:1326-1334. |
| 52 | Chen F, Dudhia J.Coupling an advanced land surface-hydrology model with the Penn State-NCAR MM5 modeling system.Part I:model implementation and sensitivity[J].Monthly Weather Review,2001,129(4):569-585. |
| 53 | Hong S Y, Noh Y, Dudhia J.A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes[J].Monthly Weather Review,2006,134(9):2318-2341. |
| 54 | Stauffer D R, Seaman N L.Use of four-dimensional data assimilation in a limited-area mesoscale model.Part I:experiments with synoptic-scale data[J].Monthly Weather Review,1990,118(6):1250-1277. |
| 55 | Kalnay E, Kanamitsu M, Kistler R,et al.The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project[J].Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society,1996,77(3):437-472. |
| 56 | Berrisford P, Dee D, Fielding K,et al.The ERA-interim archive[J].ERA Report Series,2009(1):1-16. |
| 57 | Xu Z F, Han Y, Tam C Y,et al.Bias-corrected CMIP6 global dataset for dynamical downscaling of the historical and future climate (1979-2100)[J].Scientific Data,2021,8(1):293. |
| 58 | 胡芩,姜大膀,范广洲.CMIP5全球气候模式对青藏高原地区气候模拟能力评估[J].大气科学,2014,38(5):924-938. |
| 59 | Wu J, Gao X J, Giorgi F,et al.Changes of effective temperature and cold/hot days in late decades over China based on a high resolution gridded observation dataset[J].International Journal of Climatology,2017,37:788-800. |
| 60 | Taylor K E.Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2001,106(D7):7183-7192. |
| 61 | White S M, Ravelo A C, Polissar P J.Dampened El Niño in the early and mid‐Holocene due to insolation‐forced warming/deepening of the thermocline[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2018,45(1):316-326. |
| 62 | Meng X, Lyu S, Zhang T,et al.Simulated cold bias being improved by using MODIS time-varying albedo in the Tibetan Plateau in WRF model[J].Environmental Research Letters,2018,13(4):044028. |
| 63 | Huang D, Gao S B.Impact of different cumulus convective parameterization schemes on the simulation of precipitation over China[J].Tellus A:Dynamic Meteorology and Oceanography,2017,69(1):1406264. |
| 64 | Yue S Y, Yang K, Lu H,et al.Representation of stony surface‐atmosphere interactions in WRF reduces cold and wet biases for the southern Tibetan Plateau[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2021,126(21):e2021JD035291. |
| 65 | Yan D D, Liu T Y, Dong W J,et al.Integrating remote sensing data with WRF model for improved 2-m temperature and humidity simulations in China[J].Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans,2020,89:101127. |
| 66 | Gao Y H, Xu J, Chen D.Evaluation of WRF mesoscale climate simulations over the Tibetan Plateau during 1979-2011[J].Journal of Climate,2015,28(7):2823-2841. |
| 67 | Gao Y H, Chen F, Jiang Y.Evaluation of a convection-permitting modeling of precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau and its influences on the simulation of snow-cover fraction[J].Journal of Hydrometeorology,2020,21(7):1531-1548. |
| 68 | Ji Z M, Kang S C.Double-nested dynamical downscaling experiments over the Tibetan Plateau and their projection of climate change under two RCP scenarios[J].Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences,2013,70(4):1278-1290. |
| 69 | Li P X, Furtado K, Zhou T J,et al.Convection‐permitting modelling improves simulated precipitation over the central and eastern Tibetan Plateau[J].Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society,2021,147(734):341-362. |
| [1] | 孙小霞, 冯怡琳, 王永珍, 罗维成, 杨竟艺, 史宏亮, 刘继亮. 祁连山东大河林区煤矿修复对地表甲虫多样性的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(6): 176-186. |
| [2] | 董祝雷, 姜学恭, 衣娜娜, 许志丽, 杭月荷, 于水燕. 风速和植被对内蒙古地区沙尘天气影响的数值模拟[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(6): 29-39. |
| [3] | 刘民兰, 赵洪民, 邵梅, 张龄慧, 王彬, 丁乾平, 龚丞馗, 王小军, 高斌斌, 潘文旭, 罗万银. 祁连山国家公园草原补奖政策实施效益评估[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(6): 40-50. |
| [4] | 刘洋, 王娅, 杨国靖, 周立华. 祁连山北麓生态移民工程问题分析与政策建议[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 37-47. |
| [5] | 罗维成, 赵文智, 刘继亮, 杨竟艺, 白雪莲, 魏乐民, 冯怡琳. 祁连山自然保护区煤矿修复区地表节肢动物分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(6): 165-175. |
| [6] | 陈思宇, 贯雅雯, 赵丹, 娄高僮, 陈渔. 东亚沙尘气候效应对地面温度日较差影响的数值模拟[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(3): 127-138. |
| [7] | 苏昊海, 张小芳, 牛亚琳, 王海茹, 曹建军. 祁连山狼毒(Stellera chamaejasme)叶片生态化学计量特征对海拔的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(6): 205-212. |
| [8] | 高海宁, 李彩霞, 孙小妹, 张勇, 陈年来. 祁连山北麓不同海拔土壤化学计量特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(1): 219-227. |
| [9] | 刘芳, 曹广超, 曹生奎, 杨羽帆. 祁连山南坡主要流域河水稳定同位素特征及补给关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(6): 151-161. |
| [10] | 芦倩, 李毅, 刘贤德, 赵维俊. 祁连山排露沟流域青海云杉(Picea crassifolia)林土壤水分特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(5): 142-148. |
| [11] | 衣娜娜, 姜学恭, 董祝雷, 于水燕, 康晟炜. 内蒙古一次沙尘过程的数值模拟[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(3): 115-126. |
| [12] | 王宝, 王涛, 王勤花, 王鹏龙, 徐冰鑫, 高峰. 关于确保甘肃省祁连山生态保护红线落地并严守的科技支撑建议[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(1): 7-11. |
| [13] | 康丽泰, 陈思宇. 中国北方一次沙尘天气过程的数值模拟[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(2): 321-331. |
| [14] | 朱猛, 刘蔚, 秦燕燕, 曹建军, 李会亚, 赵玉. 祁连山森林草原带坡面尺度土壤有机碳分布[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(3): 741-748. |
| [15] | 赵珍, 贾文雄, 张禹舜, 刘亚荣, 陈京华. 祁连山区植被物候遥感监测与变化趋势[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(5): 1388-1395. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn

